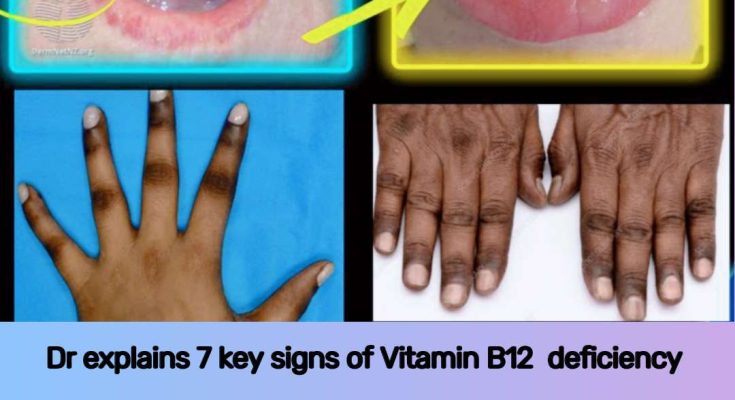
A deficiency in Vitamin B12 can indeed lead to a wide range of symptoms, impacting various bodily systems, including the mouth, skin, and nervous system. Here are 7 key signs, as explained by medical professionals, with additional detail:
- Angular Cheilitis (Stomatitis): This presents as painful cracks, inflammation, and sometimes bleeding at the corners of the mouth. While it can be caused by various factors, including other B vitamin deficiencies (like B2/riboflavin), it’s a known oral manifestation of B12 deficiency.
- Glossitis: This refers to inflammation of the tongue, often making it appear sore, red, swollen, and smooth. In severe cases of B12 deficiency, the tongue can be described as “beefy” or “fiery red” due to the loss of papillae (small bumps on the tongue’s surface). This can make eating and speaking difficult.
- Mouth Ulcers (Aphthous Ulcers): Recurrent sores or ulcers inside the mouth are another common oral symptom of B12 deficiency. The body needs B12 for proper cell division and repair, and a deficiency can affect the rapid cell turnover in the mucous membranes of the mouth, leading to ulcer formation.
- Diarrhea: Vitamin B12 deficiency can affect the gastrointestinal tract, leading to symptoms like diarrhea, as well as nausea and vomiting. This can be particularly pronounced in cases of malabsorption where the body struggles to absorb B12 from food.
- Pigmentation of the Hands and Nails (Hyperpigmentation): B12 deficiency can lead to changes in skin pigmentation, including hyperpigmentation (darkening of the skin), particularly on the hands and nails. This is thought to be related to the role of B12 in melanin production. The skin may also take on a pale yellow tinge overall.
- Jaundice: In more severe cases, B12 deficiency can cause jaundice. This is because B12 deficiency can lead to megaloblastic anemia, where red blood cells are abnormally large and don’t function properly. The destruction of these abnormal red blood cells can increase bilirubin levels in the blood, leading to a yellowish discoloration of the skin and the whites of the eyes.
- Neurological Symptoms: This is a broad category, and B12 deficiency is notorious for causing neurological problems that can range from mild to severe. These can include:
- Pins and needles (paresthesia): A tingling or prickling sensation, often in the hands and feet.
- Muscle weakness: General weakness and sometimes difficulty with coordination (ataxia).
- Memory problems, confusion, and cognitive decline: B12 is essential for brain health and nerve function.
- Vision problems: Disturbed or blurred vision.
- Mood changes: Irritability, depression, and even psychosis in severe cases.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can develop gradually and may overlap with other conditions. If you suspect a vitamin B12 deficiency, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis through blood tests and appropriate treatment, as prolonged deficiency can lead to irreversible neurological damage.